Ciprofloxacin is used in the treatment of infections from a wide range of aerobic gram-positive and aerobic gramnegative microorganisms. It has been shown to be effective against inhalational anthrax and reduce the incidence or progression of disease following exposure to aerosolized Bacillus anthracis. It is also used in select respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, typhoid fever, some sexually transmitted diseases, and septicemia. Infectious diarrhea may be caused by organisms found in food or water and transferred by person-to-person contact. This may have a devastating effect, globally, especially in immunocompromised individuals. Ciprofloxacin is effective against those organisms that may contribute to infectious diarrhea, such as Escherichia coli (enterotoxigenic strains), Campylobacter jejuni, and select strains of Shigella; and is utilized when antibacterial therapy is medically indicated. Ciprofloxacin has also been utilized as a secondary agent in the treatment of tuberculosis
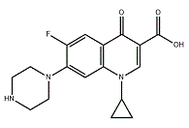
Ciprofloxacin is a synthetic third-generation quinolone antibacterial drug with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity and good bactericidal effect. Its antibacterial activity against almost all bacteria is 2 to 4 times stronger than that of norfloxacin and enoxacin.